Introduction
This describes performance improvements from changes in the v2 Google patch. While the changes improve performance in many cases, a lot of work remains to be done. It improves performance on SMP servers by:
- disabling the InnoDB memory heap and associated mutex
- replacing the InnoDB rw-mutex and mutex on x86 platforms
- linking with tcmalloc
Database reload
This displays the time to reload a large database shard on a variety of servers (HW + SW). Unless otherwise stated, my.cnf was optimized for a fast (but unsafe) reload with the following values. Note that
- innodb_flush_method=nosync is only in the Google patch and is NOT crash safe (kind of like MyISAM). This uses a real data set that produces a 100GB+ database.
- innodb_log_file_size=1300M
- innodb_flush_method=nosync
- innodb_buffer_pool_size=8000M
- innodb_read_io_threads=4
- innodb_write_io_threads=2
- innodb_thread_concurrency=20
The smpfix RPM is MySQL 5.0.37 plus the v1 Google patch and the SMP fixes that include:
- InnoDB mutex uses atomic ops
- InnoDB rw-mutex uses lock free methods to get and set internal lock state
- tcmalloc is used in place of glibc malloc
- the InnoDB malloc heap is disabled
The servers are:
- 8core - the base RPM on an 8-core x86 server
- 4core-128M - the base RPM on a 4-core x86 server with innodb_log_file_size=128M
- 8core-tc4 - the base RPM on an 8-core x86 server with innodb_thread_concurrency=4
- smpfix-128M - the smpfix RPM with innodb_log_file_size=128M
- 4core - the base RPM on a 4-core x86 server
- smpfix-4core - the smpfix RPM on a 4-core x86 server
- smpfix-512M - the smpfix RPM on an 8-core x86 server with innodb_log_file_size=512M
- smpfix - the smpfix RPM on an 8-core x86 server
- onlymalloc - the base RPM on an 8-core x86 server with the InnoDB malloc heap disabled
- smpfix-notcmalloc - the smpfix RPM on an 8-core x86 server without tcmalloc
The x-axis is time so larger is slower.
Sysbench readwrite
Sysbench includes a transaction processing benchmark. The readwrite version of the sysbench OLTP test is measured here using 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32 and 64 threads.
The sysbench command line options are:
# N is 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32 and 64The my.cnf options are:
--test=oltp --oltp-table-size=1000000 --max-time=600 --max-requests=0 --mysql-table-engine=innodb --db-ps-mode=disable --mysql-engine-trx=yes --num-threads=N
innodb_buffer_pool_size=8192MThe servers are:
innodb_log_file_size=1300M
innodb_read_io_threads = 4
innodb_write_io_threads = 4
innodb_file_per_table
innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit=2
innodb_log_buffer_size = 200m
innodb_thread_concurrency=0
log_bin
key_buffer_size = 50m
max_heap_table_size=1000M
max_heap_table_size=1000M
tmp_table_size=1000M
max_tmp_tables=100
- base - MySQL 5.0.37 without the smp fix
- tc4 - MySQL 5.0.37 without the smp fix, innodb_thread_concurrency=4
- smpfix - MySQL 5.0.37 with the smp fix and tcmalloc
- notcmalloc - MySQL 5.0.37 with the smp fix, not linked with tcmalloc
- onlymalloc - MySQL 5.0.37 with the InnoDB malloc heap disabled
- my4026 - unmodified MySQL 4.0.26
- my4122 - unmodified MySQL 4.1.22
- my5067 - unmodified MySQL 5.0.67
- my5126 - unmodified MySQL 5.1.26
- goog5037 - the same as base, MySQL 5.0.37 without the smp fix
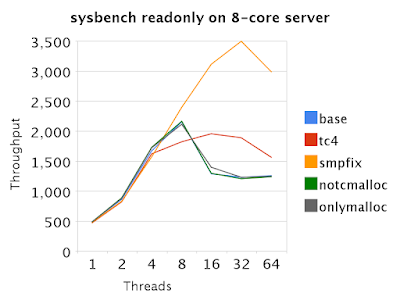
Results for sysbench readonly
Sysbench includes a transaction processing benchmark. The readonly version of the sysbench OLTP test is measured here using 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32 and 64 threads.
The sysbench command line options are:
# N is 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32 and 64The my.cnf options are:
--test=oltp --oltp-read-only --oltp-table-size=1000000 --max-time=600 --max-requests=0 --mysql-table-engine=innodb --db-ps-mode=disable --mysql-engine-trx=yes --num-threads=N
innodb_buffer_pool_size=8192MThe servers are:
innodb_log_file_size=1300M
innodb_read_io_threads = 4
innodb_write_io_threads = 4
innodb_file_per_table
innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit=2
innodb_log_buffer_size = 200m
innodb_thread_concurrency=0
log_bin
key_buffer_size = 50m
max_heap_table_size=1000M
max_heap_table_size=1000M
tmp_table_size=1000M
max_tmp_tables=100
- base - MySQL 5.0.37 without the smp fix
- tc4 - MySQL 5.0.37 without the smp fix, innodb_thread_concurrency=4
- smpfix - MySQL 5.0.37 with the smp fix and tcmalloc
- notcmalloc - MySQL 5.0.37 with the smp fix, not linked with tcmalloc
- onlymalloc - MySQL 5.0.37 with the InnoDB malloc heap disabled
- my4026 - unmodified MySQL 4.0.26
- my4122 - unmodified MySQL 4.1.22
- my5067 - unmodified MySQL 5.0.67
- my5126 - unmodified MySQL 5.1.26
- goog5037 - the same as base, MySQL 5.0.37 without the smp fix
Concurrent joins
This test runs a query with a join. It is run using concurrent sessions. The data fits in the InnoDB buffer cache. The query is:
select count(*) from T1, T2 where T1.j > 0 and T1.i = T2.iThe data for T1 and T2 matches that used for the sbtest table by sysbench. This query does a full scan of T1 and joins to T2 by primary key.
The servers are:
- base - MySQL 5.0.37 without the smp fix
- tc4 - MySQL 5.0.37 without the smp fix, innodb_thread_concurrency=4
- smpfix - MySQL 5.0.37 with the smp fix and tcmalloc
- notcmalloc - MySQL 5.0.37 with the smp fix, not linked with tcmalloc
- onlymalloc - MySQL 5.0.37 with the InnoDB malloc heap disabled
- my4026 - unmodified MySQL 4.0.26
- my4122 - unmodified MySQL 4.1.22
- my5067 - unmodified MySQL 5.0.67
- my5126 - unmodified MySQL 5.1.26
- goog5037 - the same as base, MySQL 5.0.37 without the smp fix
I only have results for 8 and 16 core servers here. Lower times are better.
With data from the worst case:
Without data from the worst case:
With data from the worst case:
Without data from the worst case:
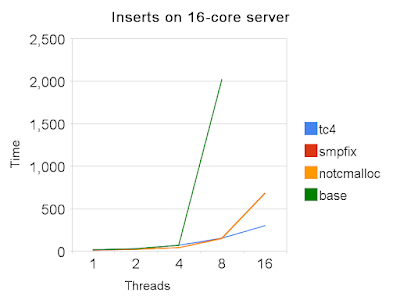
Concurrent inserts
This test reloads tables in parallel. Each connection inserts data for a different table. Tests were run using 1, 2, 4, 8 and 16 concurrent sessions. The regression for 5.0.37 is in the parser and was fixed by 5.0.54. A separate table is used for each connection. DDL for the tables is:
create table T$i (i int primary key, j int, index jx(j)) engine=innodbMulti-row insert statements are used that insert 1000 rows per insert statement. Auto-commit is used. The insert statements look like:
INSERT INTO T1 VALUES (0, 0), (1, 1), (2, 2), ..., (999,999);The servers are:
- base - MySQL 5.0.37 without the smp fix
- tc4 - MySQL 5.0.37 without the smp fix, innodb_thread_concurrency=4
- smpfix - MySQL 5.0.37 with the smp fix and tcmalloc
- notcmalloc - MySQL 5.0.37 with the smp fix, not linked with tcmalloc
- onlymalloc - MySQL 5.0.37 with the InnoDB malloc heap disabled
- my4026 - unmodified MySQL 4.0.26
- my4122 - unmodified MySQL 4.1.22
- my5067 - unmodified MySQL 5.0.67
- my5126 - unmodified MySQL 5.1.26
- goog5037 - the same as base, MySQL 5.0.37 without the smp fix
MySQL 5.0.37 has a performance regression in the parser. This was fixed in 5.0.54. See bug 29921.
Note, lower values for Time are better.
With data from the worst case:
Without data from the worst case:
With data from the worst case:
Without data from the worst case:















No comments:
Post a Comment