This post has benchmark results for RocksDB 8.5 through 8.8 using a small server. I previously wrote about results for this benchmark on a large server.
RocksDB 8.6 changes how prefetching is implemented for storage reads done by compaction. It now uses the readahead system call on Linux (see here and here) and the amount to prefetch is determined by the compaction_readahead_size option. There are/were two issues and RocksDB issue 12308 is open for this:
- db_bench in 8.6 and earlier releases uses a default of 0 for compaction_readahead_size which clobbered the new default of 2MB, leading to too-small prefetch requests. This is fixed in 8.7.
- db_bench in 8.6+ uses readahead and it appears that the performance on the overwrite benchmark step suffers with buffered IO when the value of compaction_readahead_size is larger than the value of max_sectors_kb for the underlying storage devices. When RAID is used I am not sure if compaction_readahead_size should be less than the smallest value of max_sectors_kb from any of the underlying devices or less than the sum.
- While reducing compaction_readahead_size fixes the perf regression for the overwrite benchmark step with buffered IO it introduces a perf regression of up to 6% for other read+write benchmark steps. Reducing compaction_readahead_size also hurts perf with O_DIRECT, which doesn't use the readahead syscall and benefits from a larger prefetch size. I am curious if the large reads done by compaction when compaction_readahead_size is 480KB interfere (make slower) the user reads.
tl;dr, for now ...
- Set compaction_readahead_size to be <= max_sectors_kb if using buffered IO
- Keep the default for compaction_readahead_size if using O_DIRECT
Updates
Fixed a typo: s/min_sectors_kb/max_sectors_kb/g
Benchmark
The benchmark used the Beelink server explained here that has 8 cores, 16G RAM and 1TB of NVMe SSD with XFS and Ubuntu 22.04 with the 5.15.0-79-generic kernel. There is just one storage device and no RAID. The value of max_sectors_kb is 512.
I used my fork of the RocksDB benchmark scripts that are wrappers to run db_bench. These run db_bench tests in a special sequence -- load in key order, read-only, do some overwrites, read-write and then write-only. The benchmark was used 1 client thread. How I do benchmarks for RocksDB is explained here and here.
The benchmark was repeated in three setups:
- cached - database fits in the RocksDB block cache
- iobuf - IO-bound, working set doesn't fit in memory, uses buffered IO
- iodir - IO-bound, working set doesn't fit in memory, uses O_DIRECT
Results
All of the charts below use QPS relative to 8.5.4 which is: (QPS for $me / QPS for RocksDB 8.5.4) where $me is some other version of RocksDB. Normalizing throughput like this makes it easy to see changes in performance.
The charts have results for the following. Note that max_sectors_kb is 512 so I reduced compaction_readahead_size to 480KB for some of the tests:
- 8.6.7 - RocksDB 8.6.7 as-is
- 8.7.2-2mb - RocksDB 8.7.2 with compaction_readahead_size=2MB (default)
- 8.7.2-480kb - RocksDB 8.7.2 with compaction_readahead_size=480KB
- 8.8.0-2mb - RocksDB 8.8.0 with compaction_readahead_size=2MB (default)
- 8.8.0-480kb - RocksDB 8.8.0 with compaction_readahead_size=480KB
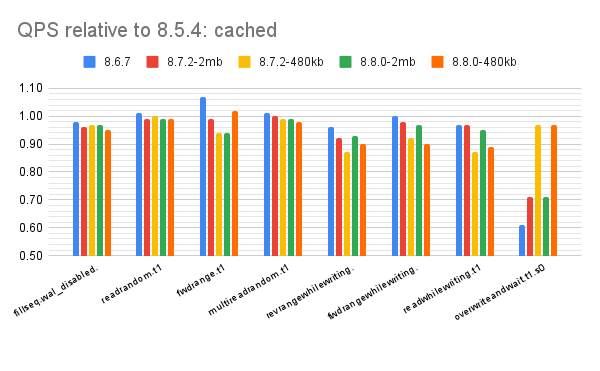
For a cached workload the QPS for overwrite ...
- Drops in 8.6.7 because it uses compaction_readahead_size=0 (a bug, fixed in 8.7)
- Drops by ~30% in 8.7 and 8.8 when compaction_readahead_size is larger than max_sectors_kb
Reducing compaction_readahead_size fixes performance for overwrite but reduces perf on the read+write benchmark steps by between 3% and 10%. The benchmark steps are revrangewhilewriting, fwdrangewhilewriting and readwhilewriting.
For the IO-bound workload with buffered IO the QPS for overwrite ...
- Drops in 8.6.7 because it uses compaction_readahead_size=0 (a bug, fixed in 8.7)
- Drops by ~10% in 8.7 and 8.8 when compaction_readahead_size is larger than max_sectors_kb
Reducing compaction_readahead_size fixes performance for overwrite but reduces perf on the read+write benchmark steps by between 3% and 5%. The benchmark steps are revrangewhilewriting, fwdrangewhilewriting and readwhilewriting.
For the IO-bound workload with O_DIRECT the QPS for overwrite ...
- Drops in 8.6.7 because it uses compaction_readahead_size=0 (a bug, fixed in 8.7)
- Drops by between 3% and 5% in 8.7 and 8.8 when compaction_readahead_size is reduced to be small than max_sectors_kb. The issue with a too-large value for compaction_readahead_size is only there when buffered IO is used.
Reducing compaction_readahead_size fixes performance for overwrite but reduces perf on the read+write benchmark steps by between 3% and 6%. The benchmark steps are revrangewhilewriting, fwdrangewhilewriting and readwhilewriting.
Debugging this for overwrite
This benchmark step only does Put operations, so the only storage reads are for compaction.
From iostat collected during the overwriteandwait benchmark step I see:
- read request sizes (rareqsz) are too small when buffered IO is used and compaction_read_ahead_size is larger than max_sectors_kb. Below it is 10.5KB for the cached workload and 5.6KB for the IO-bound with buffered IO workload. The rareqsz increases to ~400KB when compaction_readahead_size is reduced to 480KB.
- When O_DIRECT is used then the rareqsz increases by ~10% (from ~400KB to ~440KB) when compaction_readahead_size is reduced from 2MB to 480KB but throughput for overwrite, as mentioned above, also drops by ~5%.
Legend:
* rps - average value for iostat's r/s
* rmbps - average value for iostat's rMB/s
* rrqmps - average value for iostat's rrqm/s
* rawait - average value for iostat's r_await
* rareqsz - average value for iostat's rareq-sz, in KB
* version - RocksDB version
byrx
rps rmbps rrqmps rawait rareqsz version
8089 83.2 0.00 0.07 10.5 8.7.2-ra2mb
217 82.3 0.00 0.42 418.0 8.7.2-ra480kb
iobuf
rps rmbps rrqmps rawait rareqsz version
8436 48.8 0.00 0.04 5.6 8.7.2-ra2mb
148 62.9 0.00 0.33 390.7 8.7.2-ra480kb
iodir
rps rmbps rrqmps rawait rareqsz version
660 256.6 4.51 0.63 398.0 8.7.2-ra2mb
570 244.4 0.14 0.37 439.7 8.7.2-ra480kb
rps rmbps rrqmps rawait rareqsz version
668 258.1 4.89 0.63 395.7 8.8.0-ra2mb
569 244.0 0.15 0.37 439.4 8.8.0-ra480kb
From vmstat I see
- Context switch rate is much smaller with compaction_readahead_size=480kb
- User CPU utilization is larger with compaction_readahead_size=480kb
Legend:
* cs - average context switch rate from vmstat
* us - average user CPU utilization from vmstat
* sy - average system CPU utilization from vmstat
* us+sy - sum of us and sy
* id - average idle CPU utilization from vmstat
* wa - average wait CPU utilization from vmstat
* version - RocksDB version
byrx
cs us sy us+sy id wa version
17897 16.7 14.0 30.7 67.6 7.2 8.7.2-ra2mb
2190 23.9 14.0 37.9 64.0 1.0 8.7.2-480kb
iobuf
cs us sy us+sy id wa version
18652 17.3 14.0 31.3 72.3 4.4 8.7.2-ra2mb
2346 21.7 14.0 35.7 70.8 0.6 8.7.2-480kb
iodir
cs us sy us+sy id wa version
5660 23.1 14.0 37.1 67.2 5.2 8.7.2-ra2mb
6345 22.4 14.0 36.4 67.2 6.1 8.7.2-480kb
Debugging this for readwhilewriting
This benchmark step only rate-limited Put operations and then point queries as fast as possible. There will be some reads for compaction and many more (small) reads for the point queries.
I assume that the larger compaction reads that happen with compaction_readahead_size=480kb interfere with the user reads and that would explain why QPS is slightly reduced. From the compaction IO stats for iobuf (long lines, see here) I see that compaction CPU overhead, see CompMergeCPU(sec), is similar at ~423s vs ~386s. The compaction wall clock time, see Comp(sec), is much smaller when compaction_readahead_size is 480kb, ~455s vs ~714s with it set to 2MB. This different doesn't repeat for iodir (see here).
From iostat collected during the readwhilewriting benchmark step I see:
- Average read request size (rareqsz) increases when compaction_readahead_size is reduced to be smaller than max_sectors_kb
Legend:
* rps - average value for iostat's r/s
* rmbps - average value for iostat's rMB/s
* rrqmps - average value for iostat's rrqm/s
* rawait - average value for iostat's r_await
* rareqsz - average value for iostat's rareq-sz, in KB
* version - RocksDB version
byrx
rps rmbps rrqmps rawait rareqsz version
2577 29.1 0.00 0.07 12.1 8.7.2-ra2mb
2607 39.0 0.00 0.07 17.3 8.7.2-480kb
iobuf
rps rmbps rrqmps rawait rareqsz version
10081 76.9 0.00 0.06 7.9 8.7.2-ra2mb
7370 75.5 0.00 0.07 10.8 8.7.2-480kb
iodir
rps rmbps rrqmps rawait rareqsz version
11937 80.6 0.41 0.05 7.2 8.7.2-ra2mb
11170 76.7 0.02 0.05 7.5 8.7.2-480kb
From vmstat I see
- Context switch rate is larger during iobuf (IO-bound with buffered IO) when compaction_readahead_size is 2MB.
Legend:
* cs - average context switch rate from vmstat
* us - average user CPU utilization from vmstat
* sy - average system CPU utilization from vmstat
* us+sy - sum of us and sy
* id - average idle CPU utilization from vmstat
* wa - average wait CPU utilization from vmstat
* version - RocksDB version
byrx
cs us sy us+sy id wa version
11305 6.0 14.0 20.0 82.8 7.5 8.7.2-ra2mb
11367 5.6 14.0 19.6 82.5 8.1 8.7.2-480kb
iobuf
cs us sy us+sy id wa
24476 5.2 14.0 19.2 80.9 10.2 8.7.2-ra2mb
18744 5.0 14.0 19.0 82.7 8.9 8.7.2-480kb
iodir
cs us sy us+sy id wa
25141 6.1 14.0 20.1 84.2 7.6 8.7.2-ra2mb
24524 5.9 14.0 19.9 83.9 8.0 8.7.2-480kb

.png)

%20_%20(QPS%20for%208.0.34).png)
No comments:
Post a Comment